What are the different types of five-axis machine tools?
Release time:
Mar 14,2025
What is a five-axis machine tool?
Five-axis linkage is a term in numerical control. Linkage means that the axes of a numerical control machine tool reach a certain set point simultaneously at a certain speed. Five-axis linkage is applicable to all five axes. Five-axis linkage numerical control machine tools are high-tech and high-precision machine tools specially designed for processing complex curved surfaces. This kind of machine tool system has a significant influence on industries such as aviation, aerospace, military, scientific research, precision instruments, and high-precision medical equipment in a country. The equipment manufacturing industry is the cornerstone of a country's industry, providing important means for the development of new technologies and new products and modern industrial production. It is an indispensable strategic industry. Even developed industrialized countries attach great importance to it. Five-axis linkage numerical control machine tools are high-tech and high-precision machine tools specially designed for processing complex curved surfaces. This kind of machine tool system has a significant influence on industries such as aviation, aerospace, military, scientific research, precision instruments, and high-precision medical equipment in a country.
The mechanical structure forms of five-axis machine tools are diverse, but mainly include the following types:
Compared with traditional three-axis machine tools, five-axis machine tools have numerous advantages such as improving cutting conditions, avoiding tool interference, enabling one-time clamping, enhancing processing quality and efficiency, simplifying production management, and shortening the development cycle of new products.
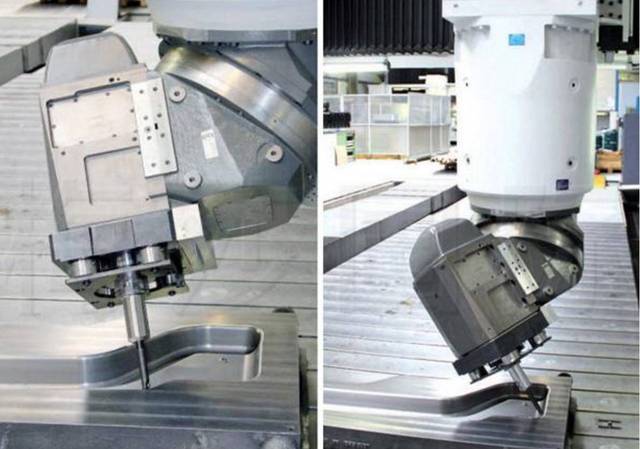

Advantages of five-axis linkage machine tools
The advantages of the five-axis linkage machine tool: it can complete the five-sided processing of the parts at one time, reduce the number of repeated clamping, improve the processing accuracy and save time.
For complex parts, multiple clamping needs to find the reference coordinates again, which will affect the positioning accuracy of processing. All processing can be completed after one positioning with the five-axis linkage machine tool. Efficient and high-precision machining of complex parts. The use of the five-axis linkage machine tool makes the clamping of the workpiece easy.
No special fixture is required during processing, which reduces the cost of fixture, avoids multiple clamping and improves the machining accuracy of die. The use of five-axis technology processing, the mold can reduce the number of fixtures used, in the mold processing can be deep cavity, deep groove processing, saving processing costs. In addition, because the five-axis machine can eliminate many special tools in the machining, the tool cost is reduced. The five-axis linkage machine tool can increase the effective cutting edge length of the tool, reduce the cutting force, improve the service life of the tool and reduce the cost. The use of five-axis linkage machine tool can quickly complete the mold processing, fast delivery, better ensure the quality of the mold processing, make the mold processing easier, and make the mold modification easier.
Using the tool shaft controllability, the side edge of the tool is cut, improving efficiency and surface quality, and extending the tool life.
The five-axis machine tool can flexibly adjust the Angle of the tool and the workpiece, and the five-axis machine tool can use the tool side edge cutting, and the processing efficiency is higher. It also reduces tool wear.
What are the types of five-axis linkage machine tools?
The five-axis machine tool was developed at the original three-axis Machining center (5 Axis Machining). According to ISO regulations, when describing the movement of CNC machine tools, the right-handed rectangular coordinate system is used; The axis parallel to the main axis is defined as the z axis, and the rotation coordinates around the x, y, and z axes are A, B, and C respectively. The movement of each axis can be achieved by the table or the movement of the tool, but the direction is defined by the direction of the tool's movement relative to the workpiece. Generally, five-axis linkage refers to the linear interpolation motion of any 5 coordinates in x, y, z, A, B, and C. In other words, five axes, x, y, z three axes of movement plus any two axes of rotation. Five axes according to the linkage axis swinging mechanism is different, there are the following categories.
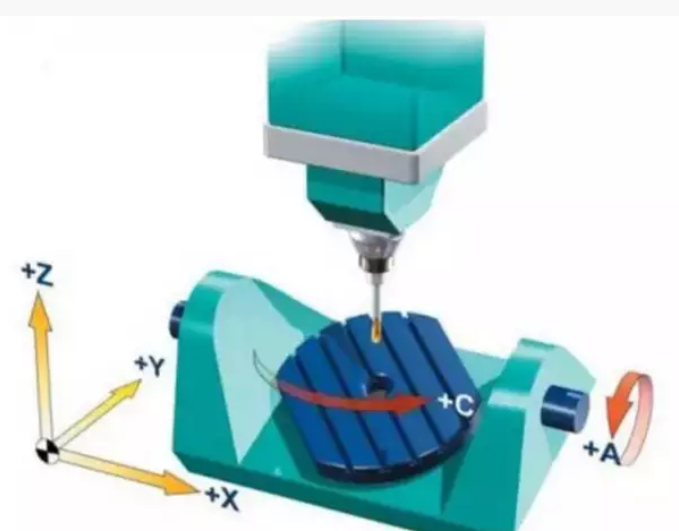

Bench cradle
Based on the basis of the traditional three-axis machining center, coupled with the cradle table, the workpiece is swung to become a 3+2 type five-axis linkage machining center. The linkage axis is X/Y/Z/A/C, and the B-axis does not rotate in the Y-axis direction.
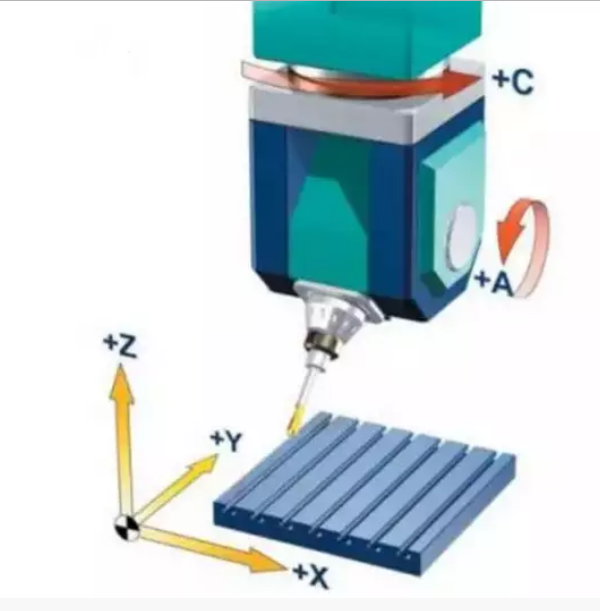

Vertical spindle double swing head
There is generally an electric spindle with a loose broach structure in the middle of the swing head, so the size of the double swing head itself is not easy to make small, plus the need for the range of activity of the double swing head, so the processing range of the five-axis linkage machine tool with the double swing head structure should not be too small, but the larger the better, generally gantry or moving beam gantry. The linkage axis is X/Y/Z/A/C, and the B-axis does not rotate in the Y-axis direction.
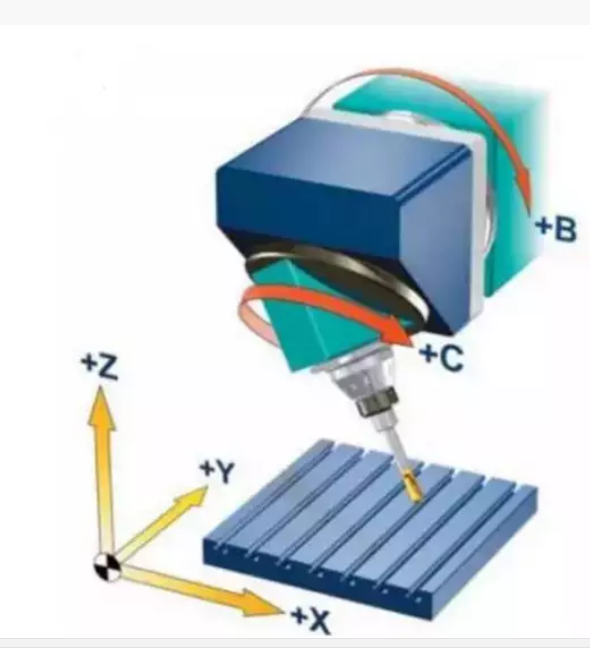
Horizontal spindle double swing head
Five-axis linkage with double swing head based on horizontal machining center structure. The linkage axis is X/Y/Z/B/C, and axis A does not rotate in the direction of the X axis.
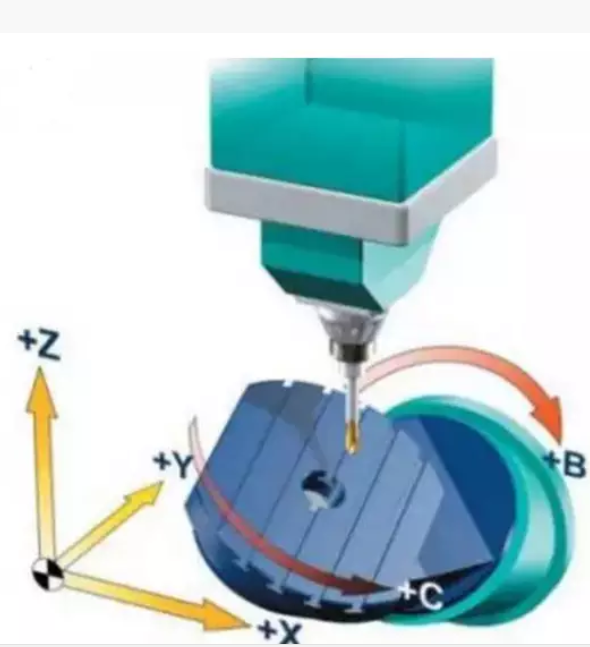
Table swing type
After the maturity of the direct drive motor, the structure of the five-axis linkage has also been greatly improved. The whole table can perform double swing. At present, the C-axis direct drive can reach a certain speed and achieve the turning effect. The linkage axis is X/Y/Z/B/C, and axis A does not rotate in the direction of the X axis.
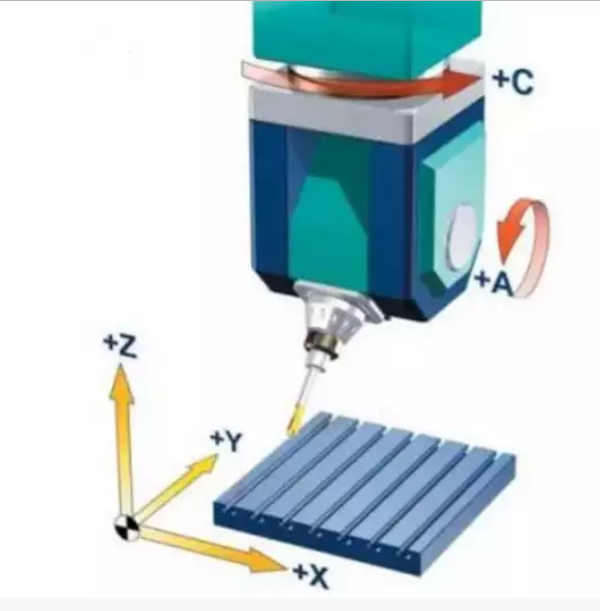

Table spindle swing
According to the evolution of the swinging mechanism, the table and the main shaft swing respectively, forming a combination of the two. The linkage axis is X/Y/Z/A/C, and the B-axis does not rotate in the Y-axis direction.
Related News







